Understanding the Mughal Empire: Growth and Legacy
Introduction
The Mughal Empire, one of the most significant empires in Indian history, flourished from the early 16th to the 19th century. Its relevance today is evident in the rich cultural heritage, architectural wonders, and the syncretic traditions that emerged during its rule. An exploration of the Mughal Empire offers insights into the socio-political and economic landscapes of the Indian subcontinent, as well as the deep-seated influences that continue to resonate in contemporary India.
The Rise of the Mughal Empire
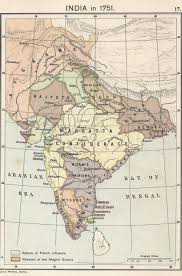
The Mughal Empire was founded by Babur in 1526 after his victory at the First Battle of Panipat. Babur, a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan, established a dynasty that would shape Indian history for over three centuries. The empire reached its zenith under Akbar the Great (1556-1605), who implemented policies of religious tolerance and administrative efficiency, allowing for social harmony among the diverse populations in his realm.
Historical Flourishment
Under Akbar and his successors, the Mughal Empire expanded its territories through strategic alliances and military campaigns. The reigns of Jahangir and Shah Jahan are particularly noted for their exceptional contributions to art, culture, and architecture. The construction of the Taj Mahal, built by Shah Jahan in memory of his wife Mumtaz Mahal, remains a symbol of the empire’s architectural brilliance and a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The Decline of the Empire
Despite its earlier successes, the Mughal Empire began to decline in the late 17th century. Factors such as administrative decay, regional rebellions, and foreign invasions contributed to its downfall. The rise of the Marathas and the European colonial powers, particularly the British, further weakened the Mughal hold on India. The last Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah II, was deposed during the Indian Rebellion of 1857, marking the end of the empire.
Legacy of the Mughal Empire
The legacy of the Mughal Empire is profound and multifaceted. Its contributions to architecture, art, and culture have left an indelible mark on Indian society. The synthesis of various cultural elements created a unique Indo-Islamic culture that persists today. Moreover, the era has influenced modern Indian politics, society, and communal relationships.
Conclusion
In summary, the Mughal Empire’s impact on India is both vast and significant. Understanding this period provides a better grasp of contemporary issues in India, including cultural diversity and historical narratives. As we reflect on this era, it is crucial to recognize how historical empires shape our present and future, making the story of the Mughal Empire vital for all who seek to understand India’s rich heritage.









