Understanding the Mughal Empire and Its Impact on India
Introduction
The Mughal Empire, which reigned over significant parts of India from the early 16th to the 19th century, continues to be a vital subject of study in understanding India’s rich history. The period is characterized by remarkable achievements in architecture, culture, and politics. The legacy of the Mughal Empire is evident in various aspects of Indian society today, making it a crucial topic for historians and enthusiasts alike.
Historical Background
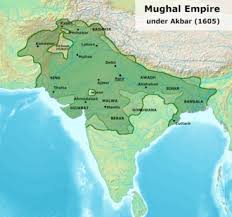
The Mughal Empire was established by Babur in 1526 after his victory in the First Battle of Panipat. The empire reached its zenith under emperors like Akbar, Jahangir, and Shah Jahan, who not only consolidated the empire’s vast territories but also fostered a culture of religious tolerance and artistic achievement. Landmark structures such as the Taj Mahal, built during Shah Jahan’s reign, exemplify the architectural prowess of this era.
Key Achievements and Cultural Contributions
One of the most significant aspects of the Mughal Empire was its promotion of cultural syncretism. The era saw the flourishing of arts, including miniature painting, poetry, and music, which combined Persian, Indian, and Islamic influences. Akbar’s policy of religious tolerance, known as Din-i Ilahi, aimed to bridge divides between Hindus and Muslims, laying the groundwork for a more unified society.
Decline of the Mughal Empire
Despite its grandeur, the Mughal Empire began to decline in the late 17th century due to several factors, including internal strife, economic difficulties, and increasing European colonial ambitions. The loosening of central control eventually led to the empire’s fragmentation, which was hastened by invasions such as that of Nadir Shah in 1739. By the mid-19th century, the empire had effectively come to an end, paving the way for British colonial rule over India.
Significance for Modern India
The Mughal Empire’s influence is still seen today in India’s architecture, cuisine, and cultural practices. The blend of cultures during this period shaped a unique Indian identity, fostering an appreciation for diversity that resonates in modern Indian society. As the country navigates its contemporary challenges, the lessons from this historical empire can serve as reminders of unity, tolerance, and cultural richness.
Conclusion
In summary, the Mughal Empire remains a significant chapter in India’s historical narrative. Its contributions to culture, architecture, and governance have left an indelible mark that continues to influence the subcontinent. As we reflect on the impact of the Mughal Empire, it is essential to recognize not only its accomplishments but also the complexities of its legacy. Understanding this era can foster a deeper appreciation of India’s multifaceted identity in the current global landscape.