Understanding the Middle East Map: A Geopolitical Overview
Introduction
The Middle East, a region bridging Europe, Asia, and Africa, holds significant geopolitical importance due to its diverse cultures, religions, and historical conflicts. Understanding the Middle East map is vital for grasping the complexities of international relations, trade routes, and regional conflicts that shape global dynamics. With ongoing changes in borders and political landscapes, a detailed look at the Middle East map is essential for academics, policymakers, and the general public alike.
Geographical Overview
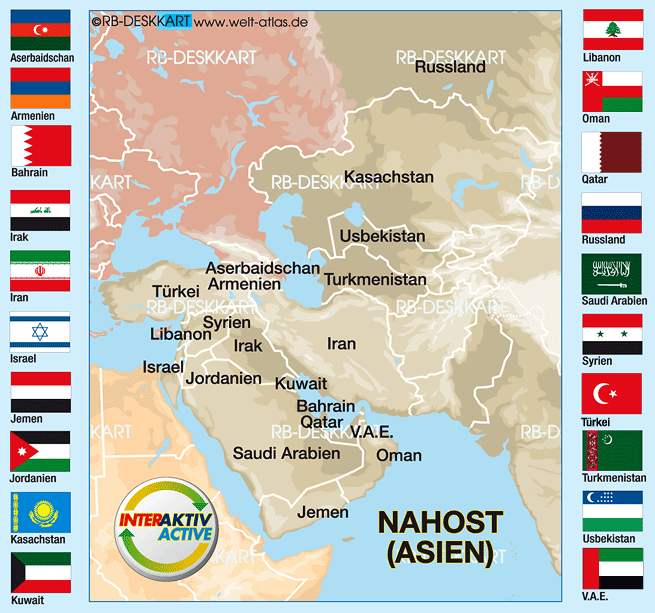
The Middle East encompasses a variety of countries, including but not limited to Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Syria, Lebanon, and the Gulf States. The region is defined not only by its borders but also by its strategic waterways, such as the Persian Gulf and the Suez Canal, which are crucial for oil transport and trade. The map of the Middle East illustrates a plethora of terrains, from deserts to mountains, further adding to the region’s diverse demographics.
Current Events and Changes
Recently, the geopolitical landscape of the Middle East has been reshaped by various events, including the ongoing conflict in Syria, tensions between Iran and Israel, and the evolving relations between Arab states and Israel, epitomized by the Abraham Accords. These developments influence both the physical borders and the political dynamics of the region as nations navigate alliances and rivalries.
Educational Importance
For students and learners, the Middle East map serves as an educational tool highlighting historical narratives, such as the ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia and the significance of trade routes traversing the region throughout history. Maps are commonly used to demonstrate the impact of colonialism, regional conflicts, and territorial disputes, providing a visual understanding of complex concepts.
Conclusion
The Middle East remains a focal point for global affairs, and understanding its map is crucial to grasp the broader implications of its geopolitical significance. As this region continues to evolve, those interested in international relations, culture, and history will benefit greatly from familiarizing themselves with the Middle East map, which is not merely a tool for navigation but a representation of a complex and dynamic world. In the years ahead, the Middle East will likely continue to capture global attention, making awareness of its maps and borders even more significant.