Understanding the GST Payment Process in India
Introduction
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) has transformed the taxation landscape in India since its implementation on July 1, 2017. This comprehensive indirect tax aimed to consolidate various central and state taxes into a single layer, making the tax system simpler and more efficient. As businesses adapt to this system, understanding the GST payment process is of paramount importance. It not only ensures compliance but also facilitates smoother operations across various sectors.
What is GST Payment?
GST payment refers to the obligation of businesses to remit the GST they collect from customers to the government, as well as the tax on their purchases. The GST is categorized into three parts: Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST), State Goods and Services Tax (SGST), and Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST). Depending on the type of transaction, businesses need to calculate their GST liability accurately to stay compliant with the law.
Steps to Make GST Payment
- Registration: Businesses must register on the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) portal and obtain a Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN).
- Calculate GST Liability: Businesses should maintain detailed records of both sales and purchases to calculate their monthly or quarterly GST liability.
- Log in to GST Portal: Once the liability is calculated, businesses can log in to the GST portal to initiate the payment.
- Make Payment: Payments can be made online through various methods such as net banking, debit/credit cards, or through the use of an Over-the-Counter facility at designated banks.
- File GST Returns: Following the payment, businesses must file their GST returns (GSTR) within the specified deadlines to ensure proper compliance.
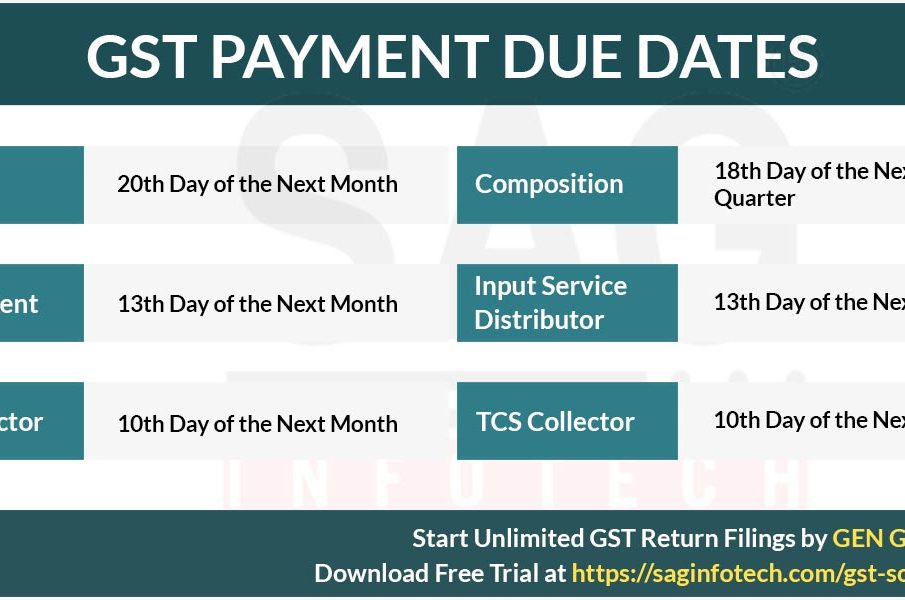
Deadlines and Compliance
One of the key aspects that businesses must monitor is the deadline for GST payment and filing returns. Typically, monthly GST returns are due on the 20th of the following month. Quarterly returns may have different deadlines, depending on the category of the taxpayer. Staying on top of these deadlines is crucial as late payments incur penalties and interest, impacting a business’s cash flow.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the GST payment process is essential for all businesses operating in India. Compliance with GST regulations not only helps avoid penalties but also contributes to the ease of doing business. As the GST system evolves, it is important for businesses to stay updated on any changes in the law, payment methods, and filing processes. By ensuring timely payments and accurate filings, businesses can operate smoothly in compliance with the Indian tax system, paving the way for sustained growth and success.








