Understanding Lyme Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Introduction
Lyme disease is an emerging infectious disease caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected black-legged ticks. Its recognition is crucial as cases have seen a significant rise in recent years, particularly in the Northeastern and North-Central United States. Understanding Lyme disease is vital for prevention and early treatment.
What Causes Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is predominantly caused by the bite of a tick that carries Borrelia burgdorferi. These ticks are often found in wooded or grassy areas. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 30,000 cases are reported annually in the United States; however, the actual number is estimated to be much higher due to underreporting. Public awareness is essential, particularly in high-risk regions where ticks are more prevalent.
Symptoms of Lyme Disease
The symptoms of Lyme disease can vary significantly among individuals and may occur in stages. Early symptoms include:
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue
- Muscle and joint aches
- Swollen lymph nodes
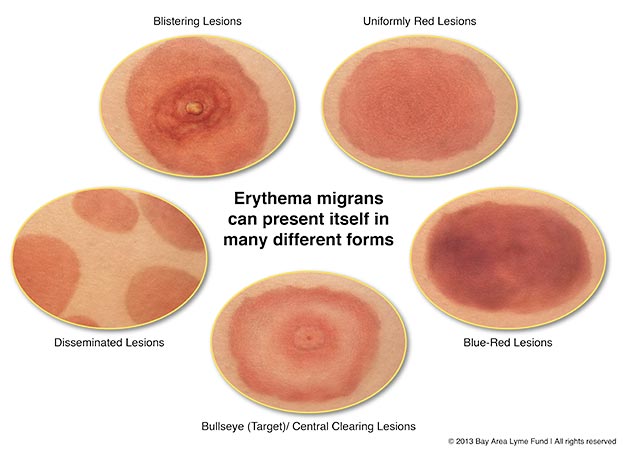
- Rash: often resembling a ‘bull’s-eye’ pattern
If untreated, Lyme disease can progress to more severe symptoms affecting the heart, joints, and nervous system, leading to complications such as arthritis or neurological disorders.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing Lyme disease primarily involves minimizing exposure to tick bites. Effective strategies include:
- Wearing long-sleeved clothing and long pants when venturing into wooded areas.
- Using insect repellents containing DEET on exposed skin.
- Performing thorough tick checks after spending time outdoors.
- Creating tick-safe zones around homes by reducing tall grasses and brush.
Conclusion
Lyme disease is a significant public health concern, particularly for those living in or visiting areas where ticks thrive. Education and awareness are paramount in reducing the incidence of the disease. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention tactics, individuals can take proactive measures to protect themselves and their families. Continued research and community initiatives are required to further combat the spread of Lyme disease and promote overall public health.









