Understanding GBS Virus: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention
Introduction to GBS Virus
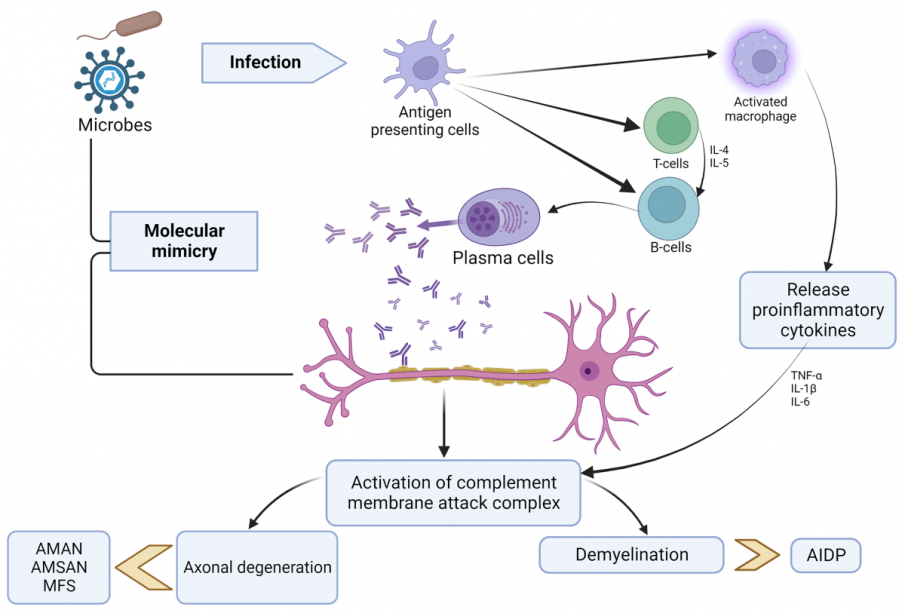
The GBS virus, known as Guillain-Barré Syndrome, is a rare neurological disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nerves. It can lead to muscle weakness or even paralysis. Understanding this virus has gained relevance in the light of recent studies and outbreaks, prompting public health initiatives to safeguard vulnerable populations.
Recent Developments and Findings
Recent reports have highlighted the correlation between GBS and various viral infections, including Zika and influenza, which raise alarm during flu seasons and outbreaks. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Neurology in mid-2023 indicated that there was a spike in GBS cases following the Zika virus outbreak several years prior. Healthcare professionals are now on alert, particularly in regions where such viruses are circulating.
In India, there have been increasing calls for awareness campaigns to educate the public on the symptoms of GBS, which can begin with weakness in the legs and can escalate to more severe complications. Increased education can be critical, especially for individuals who are at a higher risk of autoimmune disorders.
Symptoms and Risk Factors
GBS often starts with tingling sensations in the legs that may spread upwards. Other symptoms may include muscle weakness, difficulty walking, and in severe cases, respiratory failure. While the exact cause of GBS is not fully understood, certain infections like Campylobacter jejuni, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, and Zika virus have been associated with its onset.
Age and health conditions can contribute as well; older adults or individuals with certain health issues may have a higher risk of developing GBS after a viral infection.
Preventive Measures and Future Outlook
Currently, there are no definitive vaccines for GBS, but undergoing vaccination against prevalent viruses like influenza can help reduce the risk of developing it. Public health officials are emphasizing the importance of early detection and prompt medical care to mitigate the effects of GBS.
Continued research is crucial for unraveling the complexities of GBS. Understanding its triggers and developing effective prevention strategies will be key in reducing its impact on public health. Health authorities are urged to remain vigilant in monitoring outbreaks and increasing community awareness, which can ultimately save lives.
Conclusion
As our understanding of the GBS virus continues to evolve, staying informed about its symptoms and the importance of seeking timely medical help can empower individuals. While the rarity of GBS offers some comfort, the potential for outbreaks from associated viral infections necessitates ongoing vigilance. By promoting awareness and increasing research, we can better prepare and potentially overcome the challenges posed by this complex syndrome.









