Understanding Existential Threats in Today’s World
Introduction
Existential threats are events or conditions that could lead to humanity’s extinction or the irreparable decline of civilization. These threats have become increasingly relevant in modern discussions about global security, public policy, and environmental sustainability. With advances in technology and shifts in societal dynamics, humanity faces myriad challenges that pose severe risks to its existence.
Main Body
Among the most pressing existential threats is climate change, which has garnered international attention as temperatures rise and weather patterns become more unpredictable. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the world must limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius to avoid catastrophic consequences. Climate change threatens not just ecosystems, but also food security, water supply, and economic stability, thereby endangering human life on a large scale.
Another significant existential threat comes from the rise of nuclear weapons and the potential for their use in conflict. The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists notes that geopolitical tensions among nuclear-armed nations heighten the risk of a catastrophic event. The ongoing military developments and arms races could lead to dire consequences, emphasizing the need for robust diplomacy and disarmament initiatives.
Pandemics have also emerged as a notable existential threat, as evidenced by the COVID-19 crisis. The World Health Organization has highlighted how global connectivity can amplify the spread of infectious diseases, leading to widespread health crises that undermine the foundations of society. Future preparations must prioritize global health systems and equitable vaccine distribution to mitigate such risks.
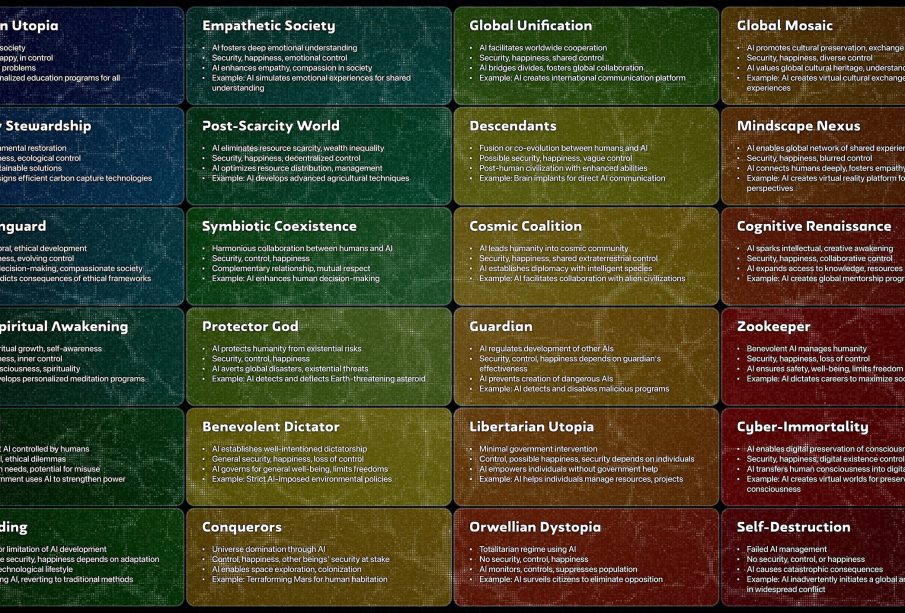
Technological advancements, particularly in artificial intelligence (AI), pose another layer of existential risk. Experts warn about the need for ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks to ensure that AI development does not lead to unintended consequences, including uncontrolled autonomous systems.Risks associated with bioengineering and synthetic biology could enable the creation of harmful pathogens, amplifying existing challenges to public safety and humanity’s survival.
Conclusion
Addressing existential threats requires unprecedented global cooperation and a multi-disciplinary approach. Governments, scientists, and civil society must work together to devise actionable strategies that can mitigate these risks effectively. The survival of humanity hinges on our ability to manage these diverse threats and implement proactive measures. The time for action is now, as the consequences of inaction could be irrevocable, challenging future generations to sustain a livable planet.









