Understanding Excessive Heat and Its Implications in India
Introduction
Excessive heat has become a pressing concern across the globe, particularly in India, where extreme temperatures are beginning to pose serious health risks, disrupt daily life, and challenge infrastructure. As climate change continues to worsen, the country experiences longer and more intense heat waves, raising alarms among health officials, policymakers, and citizens alike. Understanding the causes, effects, and preventive measures against excessive heat is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of the population.
Current Situation
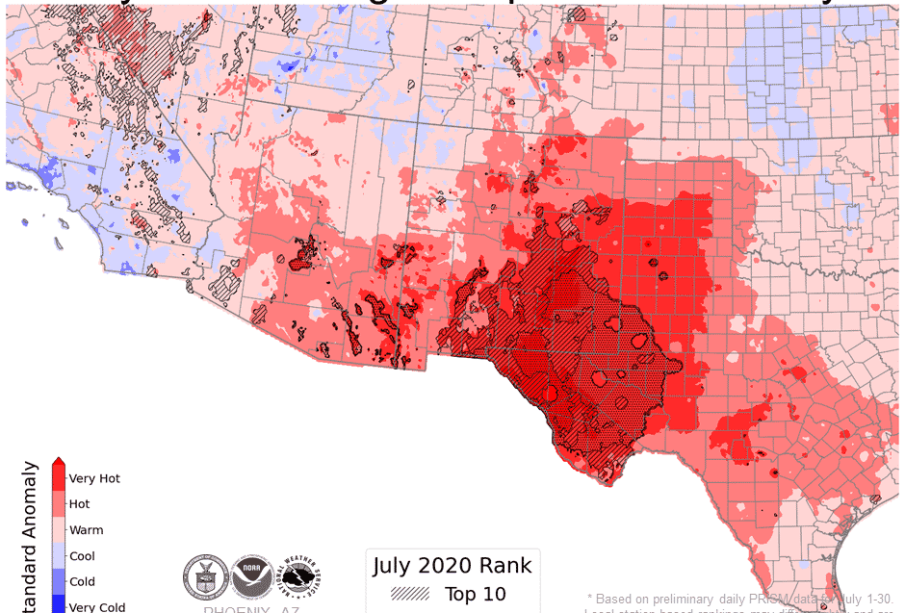
According to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), 2023 has seen unprecedented high temperatures across various states, with several regions recording temperatures above 45 degrees Celsius. The northern states, such as Rajasthan and Punjab, along with parts of central India, have been particularly affected. In many areas, schools have been shut down, and outdoor work has been restricted in an effort to protect citizens from the dangers associated with heat exhaustion and heat stroke.
The Effects of Excessive Heat
Extremely high temperatures can lead to a range of health issues, including heat exhaustion, dehydration, and even heat-related fatalities. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, those with pre-existing medical conditions, and outdoor workers, are disproportionately affected. Furthermore, excessive heat can exacerbate respiratory and cardiovascular problems, prompting local health authorities to issue warnings and establish cooling centers. The economic impact is also notable, as high heat can reduce labor productivity, strain energy resources due to increased air conditioning use, and damage crops, leading to food insecurity.
Preventive Measures
To mitigate the risks associated with excessive heat, the Indian government, along with NGOs, is actively promoting awareness campaigns that encourage individuals to stay hydrated, avoid outdoor activities during peak heat hours, and recognize the signs of heat-related illnesses. Urban planning is also being re-evaluated to include more green spaces and water bodies to combat the urban heat island effect. Additionally, meteorological services are enhancing heat wave forecasting to ensure timely alerts are issued, enabling families and businesses to take necessary precautions.
Conclusion
As the severity and frequency of excessive heat events escalate, it becomes increasingly important for Indian society to adapt and respond effectively. By prioritizing public health, infrastructure resilience, and community awareness, we can create a safer environment for all citizens. The ongoing effects of climate change and extreme weather should motivate us to adopt sustainable practices and policies that not only address immediate challenges but also contribute to long-term solutions for our country.