Materialists: Understanding Their Influence in Society

Introduction
In today’s consumer-driven world, the concept of materialism has gained significant attention, raising debates about its implications for society, values, and personal relationships. Materialists prioritize the acquisition of physical goods and wealth, which shapes their worldview and behavior. This ideology is increasingly relevant as it influences political decisions, cultural trends, and the overall economy.
Understanding Materialism
Materialism, defined as a tendency to consider material possessions and physical comfort as more important than spiritual values, is prevalent among many demographics, particularly in urban areas. Research has shown an uptrend in materialistic attitudes, especially among younger generations. For instance, a 2022 survey indicated that 61% of millennials believe that wealth equates to success, reflecting a shift in priorities over recent decades.
Recent Trends and Events
Several recent events shed light on the growing materialistic sentiment. The rise of social media, particularly platforms like Instagram and TikTok, has played a pivotal role in glamorizing consumerism. Influencers often showcase luxury items, leading followers to equate their worth with material possessions. This phenomenon has sparked discussions among psychologists and sociologists regarding the psychological implications of such beliefs.
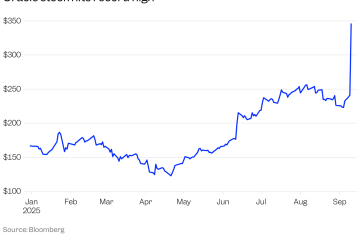
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has also resulted in shifts in materialistic values. As people experienced lockdowns, many turned to online shopping for comfort, leading to an increase in consumer spending despite economic downturns. According to a report from the Indian Economic Association, consumer goods sales in 2021 rose by 15%, driven largely by online purchases, indicating a robust materialistic trend.
Consequences of Materialism
The implications of materialism extend beyond individual consumption patterns, affecting mental health, social relationships, and environmental sustainability. Studies have shown that higher materialism is often linked to lower life satisfaction and happiness. Furthermore, consumers’ relentless pursuit of new products can lead to environmental degradation and ethical concerns surrounding production processes.
Conclusion
As society grapples with the consequences of materialism, it becomes crucial for individuals and policymakers to reflect on the long-term effects of these ideologies. The trend towards materialism shows no signs of abating, and its influence will likely continue to shape cultural and societal norms. As consumers, it is essential to balance material desires with sustainability and well-being, promoting a culture that values experiences over possessions. By fostering meaningful connections and prioritizing mental health, society can combat the often detrimental impact of materialistic values.