Maruti Suzuki and the Impact of GST Rate Changes
Introduction
Maruti Suzuki, India’s largest automobile manufacturer, has been at the forefront of the automotive industry for decades. The introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST) in July 2017 marked a significant change in the tax regime not only for car manufacturers but also for consumers. Understanding how GST rates impact Maruti Suzuki is crucial for stakeholders, including buyers, investors, and industry analysts. This article explores the implications of GST rate changes on Maruti Suzuki’s pricing and market performance.
GST Rate Changes and Their Impact
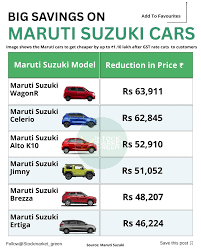
Initially, automobiles in India were subjected to a complex tax structure involving multiple taxes at state and central levels. With the implementation of GST, there was a simplification of the tax structure, where cars were classified into different tax slabs based on their category. For instance, the GST rate for small cars was set at 18%, and for larger vehicles, it could go up to 28% along with an additional cess.
In 2021, the GST council considered reducing the tax on electric vehicles from 12% to 5% to promote the green initiative. While Maruti Suzuki has a plethora of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, the company has recently made strides towards electric models, as seen with their launch plans for EVs. The reduction in GST rates can subsequently incentivize consumers to opt for electric vehicles, potentially shifting Maruti Suzuki’s product strategy.
Sales Performance Post-GST Implementation
Following the implementation of GST, Maruti Suzuki witnessed a noticeable change in sales dynamics. Initially, there was a surge in demand as buyers rushed to purchase vehicles before the tax implementation took effect. However, in the subsequent months, the sales plateaued as the market adjusted to the new pricing structure.
According to data released by the Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM), Maruti Suzuki’s market share saw fluctuations with the introduction of new competitors and changes in regulatory policies. In the fiscal year 2022-2023, Maruti Suzuki reported a growth of 22% in sales, driven by the launch of new models and adaptations to consumer preferences.
Conclusion
In summary, the impact of GST rates on Maruti Suzuki has been multifaceted. While the initial effects entailed a mixture of short-term spurts followed by adjustments, the company has adapted well by capitalizing on market trends, including the growing interest in electric vehicles. Looking ahead, changes in GST rates, particularly those favorable to EVs, could significantly influence Maruti Suzuki’s product offerings and overall sales strategies. For consumers and potential investors, staying informed about these trends will be essential for making informed decisions in the automotive market.