GBS Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Latest Developments
Introduction to GBS Disease
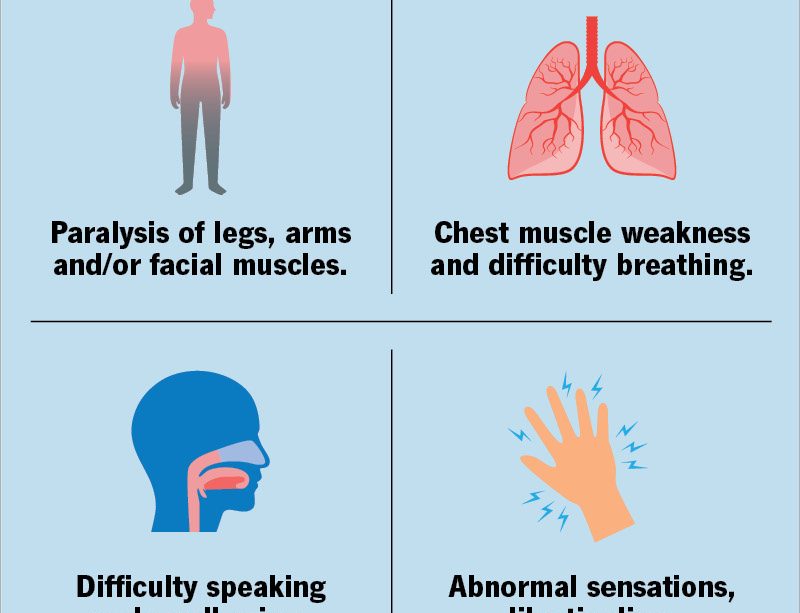
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder that leads to muscle weakness and sometimes paralysis. Understanding GBS disease is crucial, especially in light of recent epidemiological patterns and its impact on public health. The relevance of GBS disease has gained heightened attention due to studies linking infections and autoimmune responses to its onset.
Symptoms and Causes
The symptoms of GBS often begin with weakness and tingling in the legs, which can quickly spread to the upper body and arms. Many patients report flu-like symptoms prior to the onset of GBS, which may be caused by viral infections, notably the Zika virus, influenza, or even the COVID-19 virus.
The exact cause of GBS remains unidentified, but it is believed that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nerves, leading to inflammation and damage. Research is ongoing to fully uncover the mechanisms behind this syndrome.
Current Research and Developments
Recently, there has been increasing research aimed at identifying the triggers and improving treatment for GBS. A significant focus has been on post-infectious GBS cases linked to COVID-19 vaccinations. Health authorities in multiple countries emphasize that while some GBS cases have been reported after vaccination, the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks.
Moreover, clinical trials are underway to explore various therapeutic approaches including immunotherapy and physical rehabilitation methods that could enhance recovery outcomes.
Conclusion
GBS disease continues to present challenges for healthcare systems and patients alike. As awareness grows and research evolves, it is vital for individuals to recognize early symptoms and seek medical attention promptly. The future looks promising with ongoing investigations into its causes and potential treatments. With increased knowledge and proactive measures, the impact of GBS on affected individuals can be significantly mitigated. Readers are encouraged to stay informed and consult healthcare providers regarding vaccination and other preventive measures.









