An In-Depth Look at GBS Syndrome
Introduction
GBS Syndrome, or Guillain-Barré Syndrome, is an autoimmune disorder that significantly affects the peripheral nervous system. It has gained increasing attention recently due to its association with viral infections, including COVID-19. This condition causes the body’s immune system to mistakenly attack the peripheral nerves, leading to muscle weakness and, in severe cases, paralysis. With its rising incidence and impact on public health, understanding GBS Syndrome has become more critical than ever.
What is GBS Syndrome?
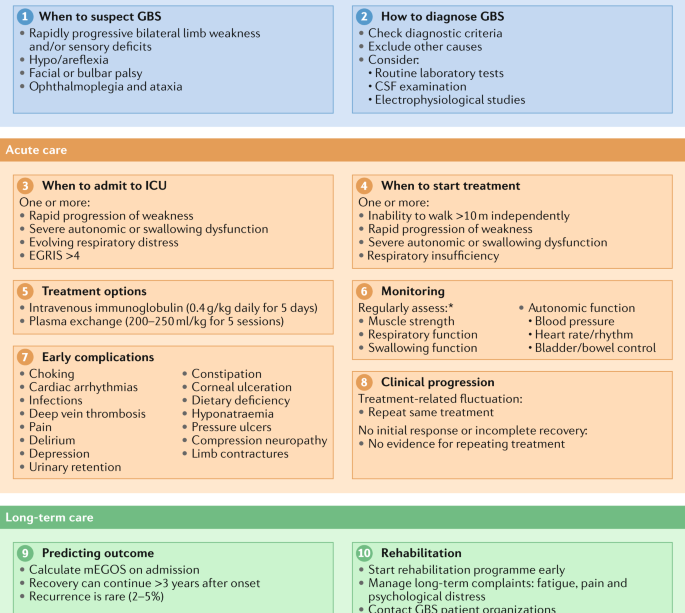
Guillain-Barré Syndrome typically begins with weakness and tingling in the legs, which can quickly progress to muscle weakness throughout the body. In some patients, it can even lead to total paralysis within days. The exact cause of GBS is still not fully understood, but it is often preceded by infections, such as respiratory or gastrointestinal infections. The relationship between GBS and recent global health crises, such as COVID-19 and influenza, has prompted further investigation into the syndrome.
Recent Developments
In recent months, healthcare professionals and researchers have reported a potential rise in GBS cases linked to the COVID-19 virus and vaccinations. The CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) has issued guidelines and monitoring protocols to observe any such correlations. They suggest that while the risk of developing GBS after a COVID-19 vaccine is extremely low, the need for increased awareness and readiness in healthcare settings has been emphasized.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of GBS Syndrome can vary widely among individuals but may include:
- Weakness in the legs progressing to the upper body
- Tingling sensations
- Difficulty walking
- Respiratory problems in severe cases
Diagnosis often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and diagnostic tests such as nerve conduction studies and lumbar punctures to analyze cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment and Prognosis
Treatment for GBS may include therapies such as plasma exchange (plasmapheresis) or intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) to reduce the immune attack on the nervous system. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving recovery outcomes, and many people gradually regain their strength over weeks to months, although some may experience lingering effects.
Conclusion
Awareness and understanding of GBS Syndrome are vital, not only for those diagnosed but also for healthcare professionals. Educational initiatives and ongoing research are essential in combating this challenging condition. As health authorities continue to monitor the links between GBS and respiratory infections, including COVID-19, it is crucial for individuals to remain informed and for researchers to keep investigating this complex syndrome. Early intervention remains a key factor in improving patient outcomes for those affected by GBS Syndrome.