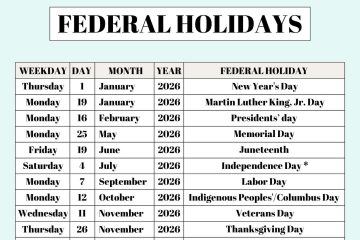
Significance and Challenges of the Brahmaputra River
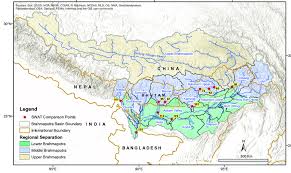
Introduction
The Brahmaputra River, one of the major rivers of the world, holds immense cultural, economic, and ecological significance in India and beyond. Originating from Tibet, this mighty river traverses through the northeastern part of India, nourishing the region’s rich biodiversity and supporting the livelihoods of millions. Its significance extends to various sectors, including agriculture, hydropower, and transportation, making it a vital lifeline for the people living alongside it.
The Journey of the Brahmaputra
Beginning from its source in Tibet, the Brahmaputra flows through Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, and then into Bangladesh, where it merges with the Ganges. Encompassing a journey of over 2,900 kilometers, the river’s basin is home to diverse flora and fauna, contributing to its UNESCO World Heritage status. The river is not only known for its economic potential but also for its cultural richness, as it plays a central role in the traditions and festivals of the communities residing along its banks.
Challenges Faced by the Brahmaputra River
Despite its significance, the Brahmaputra River faces numerous challenges. Environmental issues such as deforestation, climate change, and pollution threaten its health and the ecosystems dependent on it. Recent studies indicate erratic rainfall patterns and increased sedimentation levels due to excessive land use, which could potentially lead to flooding in the monsoon seasons, a common occurrence that severely impacts local populations and agriculture.
Conservation Efforts
Recognizing the importance of conserving the Brahmaputra, various governmental and non-governmental organizations have started initiatives aimed at preserving its ecological balance. Efforts include reforestation programs along the riverbanks, stricter regulations on industrial waste discharge, and community awareness campaigns to promote sustainable practices. Moreover, regional cooperation among the countries traversed by the river is crucial in managing its resources effectively.
Conclusion
The Brahmaputra River remains a crucial asset for India, contributing significantly to the region’s economy and ecology. As challenges mount due to environmental concerns and climate change, it becomes increasingly important for stakeholders to collaborate to ensure the river’s sustainability for future generations. The future of the Brahmaputra requires a balanced approach involving both development and conservation, underlining its significance as a lifeline for millions. Addressing these issues not only benefits local communities but also fosters regional stability and cooperation.