Overview of Middle East Countries and Their Significance
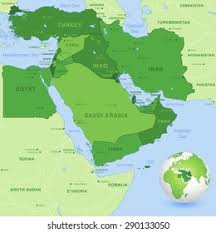
Introduction to Middle East Countries
The Middle East region comprises a diverse group of countries that play a vital role in global politics, economics, and culture. Known for its rich history and cultural heritage, the region is significant not only because of its strategic geographic location but also due to its vast oil reserves, historical conflicts, and the ongoing shifts in power dynamics.
Key Middle Eastern Countries
There are several key nations in the Middle East, including Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, United Arab Emirates, Turkey, Israel, and Egypt. Each country possesses unique characteristics and contributions to the region’s identity:
- Saudi Arabia: Known for its oil wealth, the Kingdom plays a leading role in OPEC and is also the cradle of Islam with its holy cities of Mecca and Medina.
- Iran: A pivotal player in regional politics, Iran’s influence extends across many neighboring countries, and it is a significant producer of oil and natural gas.
- Iraq: Rich in history, Iraq has been experiencing political instability, but it possesses one of the largest oil reserves in the world.
- United Arab Emirates: Comprising seven emirates, the UAE is a significant economic force, renowned for its skyscrapers and tourism.
- Turkey: Straddling Europe and Asia, Turkey’s historical role and position make it a key player in regional and international politics.
- Israel: Known for its technological innovations, Israel is a prominent player in the Middle East with ongoing conflicts impacting its relations with neighboring countries.
- Egypt: The most populous country in the Arab world, Egypt has a rich cultural heritage and is considered a moderate voice among Sunni Muslim countries.
Geopolitical Landscape
The geopolitical landscape of the Middle East is characterized by conflicts such as the Israeli-Palestinian issue, the Syrian civil war, and tensions between Iran and Saudi Arabia. These conflicts not only impact the region but also have global implications, drawing in foreign powers and shaping international relations.
Economic Significance
Economically, the Middle East is crucial due to its oil and gas reserves, which drive the global energy market. Additionally, countries are diversifying their economies; for instance, Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 aims to reduce its dependence on oil. With booming sectors like tourism, technology, and finance, the region is on the path to economic evolution.
Conclusion
The Middle East countries are integral to understanding global affairs as they continue to influence politics, economics, and culture. As these nations navigate challenges and opportunities, their future will likely shape the international landscape in the years to come. For readers, this serves as an essential insight into why the Middle East matters today and its potential trajectory in the future.