Understanding CPCB: The Central Pollution Control Board

Introduction
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) is a pivotal government body in India tasked with the responsibility of controlling and monitoring pollution levels across the nation. Established in 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, CPCB plays a crucial role in environmental conservation and public health safety. Its significance has risen in recent years, particularly given the increasing concerns about air quality and climate change.
Role and Responsibilities of CPCB
CPCB’s primary functions include setting standards, monitoring pollution levels, and implementing pollution control programs. It collaborates with state pollution control boards (SPCBs) to regulate industrial emissions and wastewater discharge, thereby playing a vital role in enforcing environmental laws. The organization also conducts research and provides technical assistance to mitigate pollution from various sources, including industries, urban development, and agriculture.
Air Quality Monitoring
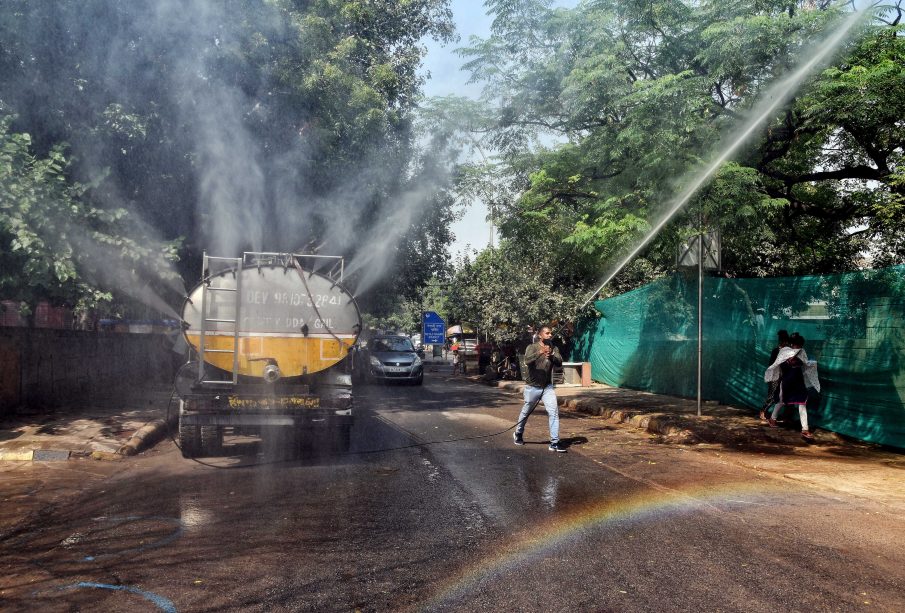
One of the key areas of CPCB’s focus is air quality monitoring. The board operates a nationwide network of air quality monitoring stations that continuously measure pollutants like PM2.5, PM10, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide. Recent data from CPCB indicates alarming levels of air pollution in metropolitan cities like Delhi, where PM2.5 levels often exceed the safe limits set by WHO. In response, CPCB has proposed several initiatives aimed at reducing vehicular emissions and promoting cleaner fuels.
Water Quality Management
CPCB also oversees the assessment of water quality in rivers, lakes, and aquifers across the country. In collaboration with various state boards, CPCB has been actively engaged in cleaning major rivers through comprehensive action plans. For instance, the Namami Gange project, aimed at rejuvenating the Ganga River, is one of the significant efforts led by the board to restore water quality.
Recent Initiatives and Developments
In light of the rising environmental challenges, CPCB has taken several proactive measures recently. It has introduced Ambient Air Quality Standards as well as guidelines for industrial effluents to enhance compliance and accountability among industries. Furthermore, CPCB has been leveraging technology by implementing real-time monitoring systems and mobile applications to facilitate better access to pollution data for citizens.
Conclusion
The Central Pollution Control Board stands at the forefront of India’s fight against pollution and environmental degradation. As urbanization and industrialization continue to rise, the responsibilities and challenges for CPCB also grow. Through rigorous monitoring and regulatory measures, CPCB plays a pivotal role in ensuring a healthier environment for future generations. The effectiveness of CPCB’s policies will significantly impact India’s journey towards sustainable development and public health safety.