Understanding the Voter List 2002 in India
Introduction
The voter list is a critical component of any democratic election, serving as the foundation for the electoral process. The voter list of 2002 is particularly significant as it reflects the demographic and political landscape of India during that period. Understanding this voter list provides insights into the electoral trends and shifts that have shaped contemporary Indian politics.
Importance of the Voter List 2002
The voter list of 2002 is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it is a historical document that showcases the electorate in India post-2000, especially after major events such as the Kargil War in 1999 and various state elections. The list represents the eligible voting population at that time, which was crucial for the elections held subsequently. Moreover, it plays a role in ensuring fair representation and accountability in governance.
Content and Composition
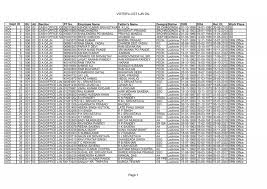
The voter list of 2002 included details regarding over a billion voters across various states and Union Territories. It categorized voters by gender, age, and locality, allowing political parties and analysts to understand voting demographics better. This information helped in strategic planning for elections, allowing parties to tailor their campaigns effectively. The Election Commission of India (ECI) periodically updates the voter list to incorporate new eligible voters and remove those who have passed away or shifted locations.
Events Surrounding the Voter List 2002
In 2002, India witnessed pivotal elections such as the Gujarat Legislative Assembly elections, which were influenced significantly by the voter demographics established in the voter list. During this time, certain regions saw increased voter turnout, reflecting public engagement influenced by local and national issues. It is also noted for the controversies and challenges regarding voter registration and the accuracy of the list, sparking debates on electoral reforms in India.
Conclusion
The voter list of 2002 holds substantial historical significance and provides a foundation for understanding the evolution of voter engagement in India. For scholars, policymakers, and citizens alike, analyzing this list allows for reflections on past electoral trends that can inform future practices and reforms. The integrity of voter lists remains crucial to the democratic process, and lessons learned from previous lists, including that of 2002, continue to shape electoral policies to enhance voter participation in India.









